The experience of math anxiety is well-documented in educational research. Physiological responses like increased heart rate and cognitive interference occur when students face mathematical tasks, particularly among underrepresented groups in STEM fields. At institutions like Prairie View A&M University, where College Algebra serves as a critical gateway course, addressing this challenge is essential for improving STEM retention rates.
Research indicates that nearly half of college students experience math anxiety, with higher prevalence among women and minority populations. Traditional lecture-based instruction often exacerbates this issue through:
- High-pressure testing environments
- Abstract presentation of concepts
- Limited opportunities for hands-on exploration
Virtual reality technology offers a promising alternative by creating immersive learning environments that address these challenges. Studies of VR-based math education demonstrate several key advantages:
- Reduced Anxiety Through Private Learning Spaces
VR headsets create individualized learning environments where students can engage with material without social pressure. Research shows this leads to decreased physiological stress markers during math tasks. - Experiential Learning of Abstract Concepts
By visualizing mathematical principles in three-dimensional space, VR helps students:
- Manipulate algebraic representations physically
- Observe real-time changes when adjusting variables
- Connect abstract concepts to concrete applications
- Improved Persistence Through Gamification
VR systems incorporate:
- Immediate feedback mechanisms
- Progressive difficulty scaling
- Visual progress tracking
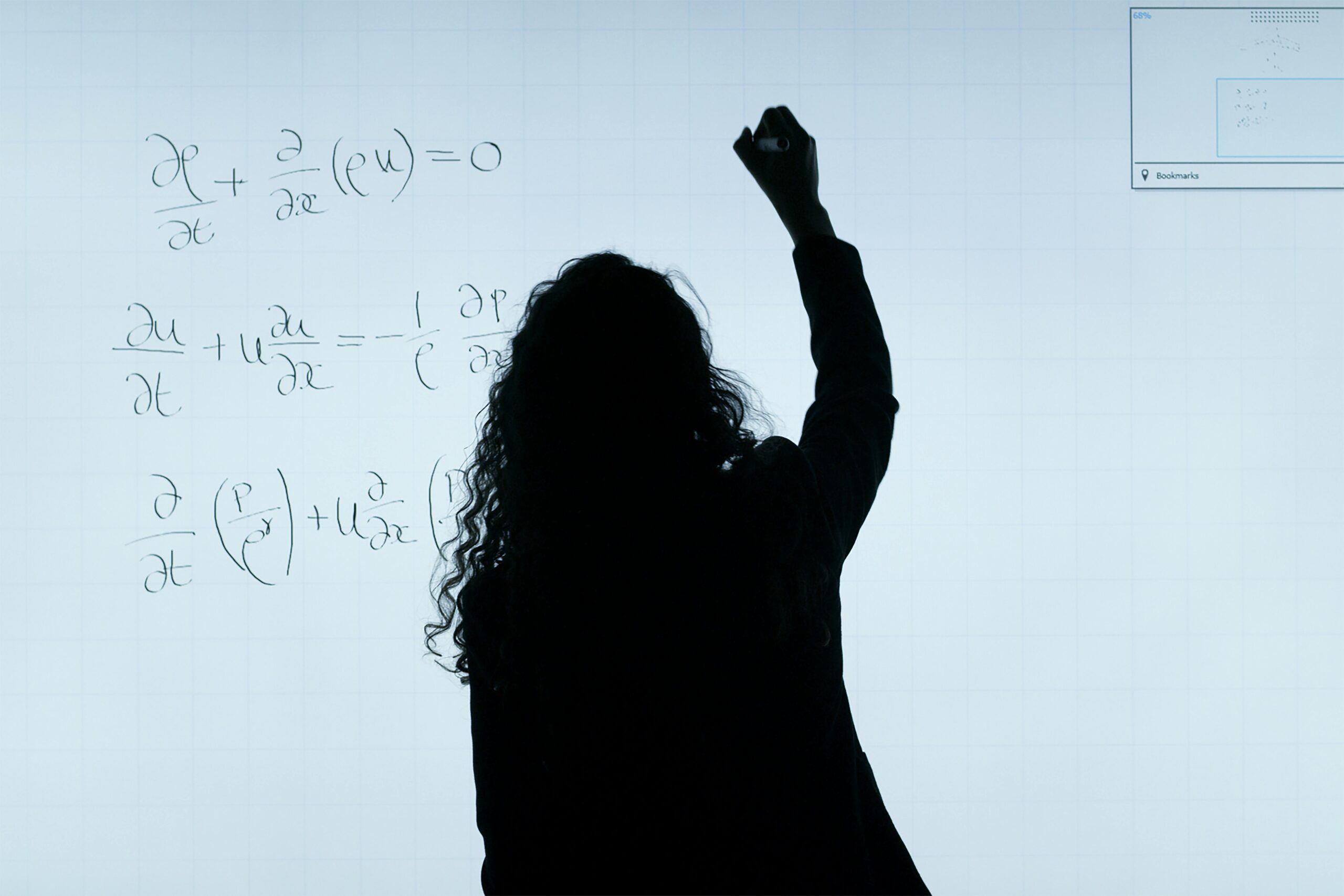
These features help students build confidence through incremental mastery rather than focusing on high-stakes assessments.
At institutions implementing VR algebra programs, preliminary data shows:
- Significant reductions in self-reported math anxiety
- Increased time-on-task for mathematical practice
- Improved pass rates in gateway courses
The potential impact extends beyond individual student outcomes. By addressing math anxiety at scale, VR technology could help:
- Increase diversity in STEM pipeline retention
- Improve graduation rates for underrepresented groups
- Change institutional approaches to mathematics instruction
As the technology becomes more accessible, key considerations for implementation include:
- Faculty training in VR pedagogy
- Hardware and software standardization
- Integration with existing curriculum frameworks
Ongoing research continues to examine:
- Long-term retention of VR-learned concepts
- Optimal balance between virtual and traditional instruction
- Cost-effectiveness at institutional scales
The development of VR mathematics education represents more than technological innovation – it offers a potential paradigm shift in how we approach one of the most persistent barriers to STEM diversity. By creating learning environments that reduce anxiety while increasing engagement, these tools may help unlock mathematical potential for students who have traditionally been underserved by conventional instructional methods.
Future directions for the field include:
- Adaptive VR systems that respond to individual learning patterns
- Expanded applications across STEM disciplines
- Integration with emerging technologies like AI tutors
While challenges remain in implementation and assessment, the demonstrated benefits of VR for reducing math anxiety suggest it will play an increasingly important role in creating more equitable STEM education pathways.



